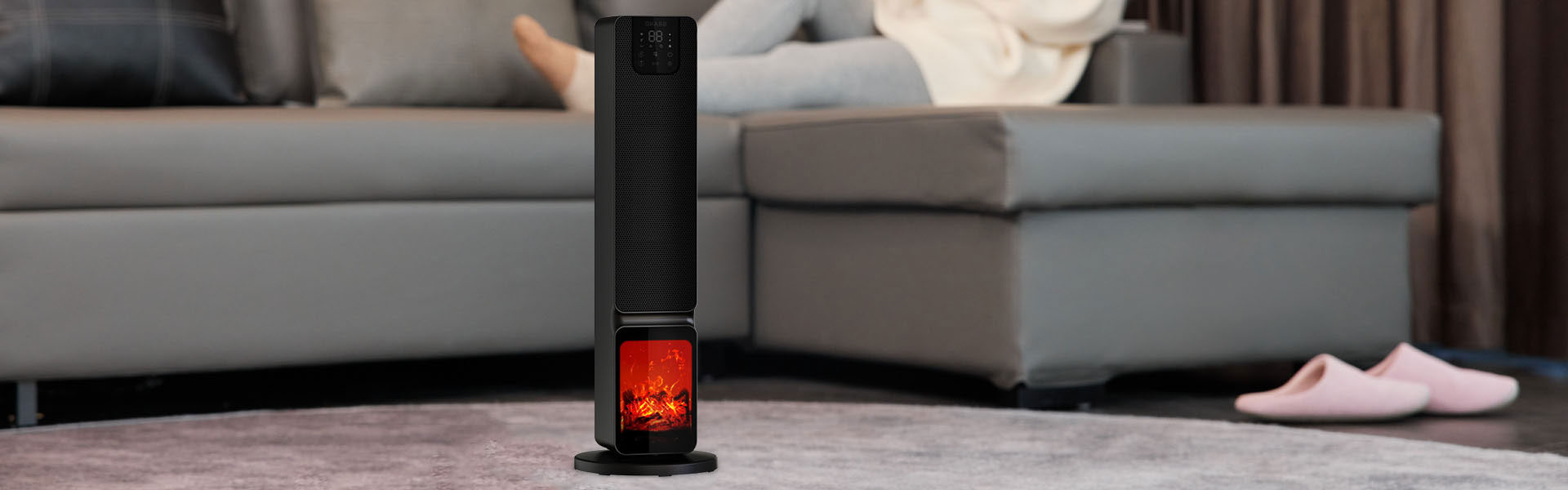
Do convector heaters use a lot of electric?
2024-11-27
Convector heaters are a popular choice for supplemental heating in various settings, from residential homes to commercial buildings. These heaters work on the principle of natural convection, utilizing air dynamics to distribute warmth efficiently. However, questions often arise about their electric consumption, particularly in terms of whether they are energy-efficient or not.
Understanding Convector Heaters
Convector heaters typically consist of an assembly of heating elements, enclosed within a casing that features an intake vent at the bottom and an exhaust vent at the top. When powered on, the heating elements warm the surrounding air, which then rises due to convection currents. The cooler air from the room is drawn in through the intake vent to replace the heated air, creating a continuous cycle that raises the room temperature.
Electric Consumption of Convector Heaters
Electric consumption of convector heaters can vary significantly based on several factors, including their wattage, operating mode, and the ambient conditions of the room. Many convector heaters offer adjustable power settings, allowing users to select a lower or higher wattage based on their heating needs. For instance, a typical convector heater might have two power settings: 1200 watts and 2200 watts.
At 1200 Watts: If a convector heater operates continuously at 1200 watts for one hour, it will consume 1.2 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity. Assuming an average electric rate of 0.12perkWh,thiswouldcostapproximately0.14 per hour.
At 2200 Watts: Similarly, running at the higher setting of 2200 watts for one hour would consume 2.2 kWh of electricity, costing around $0.26 per hour at the same electric rate.
Energy Efficiency
While the electric consumption of convector heaters can be relatively high when they are running, their energy efficiency lies in their ability to provide even and consistent heating. Unlike some other types of heaters, such as radiant heaters, which only warm objects directly in their path, convector heaters distribute heat more evenly throughout the room. This can make them more efficient in maintaining a comfortable temperature without the need for constant adjustments or additional heaters.
Factors Affecting Consumption
Room Size and Insulation: The size of the room and its insulation levels play a crucial role in determining how much energy a convector heater will consume. Larger, poorly insulated rooms will require more energy to maintain a comfortable temperature.
Climate and Outdoor Temperature: The external climate also impacts heater usage. In colder climates, heaters will need to run longer and more frequently to combat the colder temperatures.
Usage Patterns: How often and for how long the heater is used will directly affect its overall electric consumption. Using a programmable thermostat or setting timers can help manage consumption more effectively.
Conclusion
In summary, convector heaters do consume electricity, and the amount depends on various factors such as their wattage, room conditions, and usage patterns. However, their energy efficiency in distributing heat evenly throughout a space can make them a cost-effective choice for supplemental heating. By understanding their operating principles and managing their use thoughtfully, consumers can optimize their energy consumption and enjoy warm, comfortable living spaces without breaking the bank.
Ultimately, convector heaters offer a practical and effective solution for those seeking to keep their homes warm during the colder months, provided they are used wisely and within the context of a broader energy-saving strategy.

 English
English Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  Deutsch
Deutsch  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  Polski
Polski  Svenska
Svenska  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  Türkçe
Türkçe  العربية
العربية  Norsk
Norsk  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  български
български  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Română
Română 



